Turbulence modeling
From CFD-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
m (→Content of turbulence modeling section) |
m (→Content of turbulence modeling section) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
#### [[Baldwin-Barth model]] | #### [[Baldwin-Barth model]] | ||
#### [[Spalart-Allmaras model]] | #### [[Spalart-Allmaras model]] | ||
| - | #### [[Rahman-Agarwal-Siikonen Model]] | + | #### [[Rahman-Agarwal-Siikonen (RAS) Model]] |
#### [[Wray-Agarwal(WA) turbulence Model]] | #### [[Wray-Agarwal(WA) turbulence Model]] | ||
#### [[Shuai-Agarwal turbulence Model]] | #### [[Shuai-Agarwal turbulence Model]] | ||
Revision as of 19:15, 10 April 2021
Turbulence modeling is a key issue in most CFD simulations. Virtually all engineering applications are turbulent and hence require a turbulence model.
Classes of turbulence models
- RANS-based models
- Linear eddy-viscosity models
- Algebraic models
- One and two equation models
- Non-linear eddy viscosity models and algebraic stress models
- Reynolds stress transport models
- Linear eddy-viscosity models
- Large eddy simulations
- Detached eddy simulations and other hybrid models
- Direct numerical simulations
Content of turbulence modeling section
- Turbulence
- RANS-based turbulence models
- Large eddy simulation (LES)
- Detached eddy simulation (DES)
- Direct numerical simulation (DNS)
- Turbulence near-wall modeling
- Turbulence free-stream boundary conditions

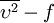 model
model
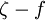 model
model