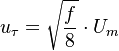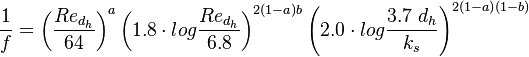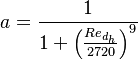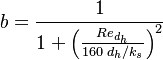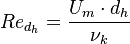Turbulence boundary conditions
From CFD-Wiki
This section is under construction, please do not trust the information available here yet
Introduction
Fully developed turbulent pipe-flow inlet
For fully developed turbulent pipe flow the turbulence inlet properties can be estimated using the model presented by Basse in Table 1 of [1].
Turbulence Intensity:
Turbulence Length-Scale:
Turbulence Energy:
Turbulence Dissipation:
The subscript 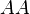 here denotes an area-averaged value. The model parameters
here denotes an area-averaged value. The model parameters 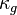 ,
,  ,
,  and
and  can be computed using the following general function:
can be computed using the following general function:
Where the a, b, c and d constants have been fitted using Princeton Superpipe measurements [2] as described in equation S44 in [3] and table 1 in [4]:
| Parameter | a | b | c | d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
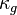 | −1.18 | 1.52 | 2.15e-4 | -8786 |
 | 2.21 | -0.60 | 3.97e-5 | 11186 |
 | 1.28 | -0.32 | 5.85e-5 | 4609 |
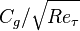 | 1.03 | -0.91 | 3.30e-5 | -11755 |
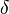 is the boundary layer thickness, which in fully developed pipe flow is the radius, or half the hydraulic diameter,
is the boundary layer thickness, which in fully developed pipe flow is the radius, or half the hydraulic diameter,  .
.
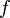 is the Darcy-Weisbach friction factor.
is the Darcy-Weisbach friction factor.
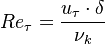 is the Reynolds number based on the friction velocity
is the Reynolds number based on the friction velocity 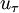 and the kinematic viscosity
and the kinematic viscosity 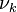 .
.
The friction velocity 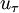 can be computed using the friction factor
can be computed using the friction factor 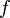 and the mean pipe flow velocity
and the mean pipe flow velocity 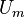 using the formula:
using the formula:
A good estimate for the friction factor 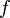 in pipe flow is Cheng's correlation [13]:
in pipe flow is Cheng's correlation [13]:
The hydraulic diameter  is the diameter of a circular pipe. For a rectangular pipe with width
is the diameter of a circular pipe. For a rectangular pipe with width 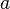 and height
and height 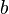 the hydraulic diameter can be computed from
the hydraulic diameter can be computed from 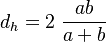 .
.
The equivalent sand-grain-roughness 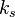 is dependent on the pipe surface properties.
is dependent on the pipe surface properties.
References
[1] Basse, N.T. (2023), "An Algebraic Non-Equilibrium Turbulence Model of the High Reynolds Number Transition Region", Water 2023, 15, 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183234.
[2] Hultmark M, Vallikivi M, Bailey SCC and Smits AJ. (2013), "Logarithmic scaling of turbulence in smooth- and rough-wall pipe flow", J. Fluid Mech. 728, 376-395.
[3] Basse, N.T. (2023), "Supplementary Information: An algebraic non-equilibrium turbulence model of the high Reynolds number transition region", https://www.researchgate.net/publication/373108195_Supplementary_Information_An_algebraic_non-equilibrium_turbulence_model_of_the_high_Reynolds_number_transition_region.
[4] Basse, N.T. (2021), "Scaling of global properties of fluctuating streamwise velocities in pipe flow: Impact of the viscous term", Physics of Fluids, vol. 33, 125109, https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.11626.

![I_{AA} = \sqrt{\left[ B_g + \frac{3}{2} A_g - \frac{8 C_g}{3 \sqrt{Re_\tau}}\right] \times \frac{f}{8}}](/W/images/math/5/e/a/5ea8b5b026dcc7448709d2dbd44a1f53.png)

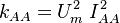
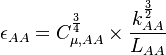
![Q(Re_\tau) = a + b \cdot tanh(c \cdot [Re_\tau - d])](/W/images/math/b/0/7/b07b24c846c7110e6d98deff6ce2ad88.png)