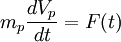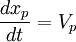Two phase flow
From CFD-Wiki
(→Importance of two phase flow in industrial configurations) |
Pejmanpark (Talk | contribs) (→References) |
||
| (287 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| - | + | article in progress | |
=== Importance of two phase flow in industrial configurations === | === Importance of two phase flow in industrial configurations === | ||
| - | Two phase flow phenomena occur in various industrial | + | Two phase flow phenomena occur in various industrial applications within all fluid mechanics application fields. |
| - | Aerospace, automotive, nuclear applications, etc. In all | + | Aerospace, automotive, nuclear applications, etc. In all these domains, it is important to predict two phase behavior. Prediction of liquid spray in an internal combustion engine allows for better control of the combustion process and helps to curtail pollutant emissions. Another important example involves steam equilibrium within a collar system; two flow analysis helps to prevent industrial accidents due to de-icing/anti-icing of aircraft on the ground etc. Any other examples can be quoted here. |
=== Overview of the different available approach === | === Overview of the different available approach === | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
== Lagrangian dispersed two-phase flow modelling == | == Lagrangian dispersed two-phase flow modelling == | ||
| + | The main goal in Lagrangien approaches is to statiscally particle history in given flow fields. | ||
| + | The starting point in Lagrangien approach is the fundamental law of dynamics: | ||
| + | :<math> | ||
| + | m_p\frac{dV_p}{dt} = F(t) | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | :<math> | ||
| + | \frac{dx_p}{dt} = V_p | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | Where <math> {F(t)} </math> stands for the resulting force on the particle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Resolution of these equations requires the knowledge of the instantaneous velocity of the fluid at particle position. The problem is thus to track fluid particles along the discrete particle trajectory. | ||
| + | A fluid particle instantaneously owns the velocity of the surrounding fluid and the simulation of its trajectory relies on a quite simple equation such as: | ||
| + | <math> {x_i(t+}{\delta}{t)}={x_i(t)}+{u_i}{\delta}{t} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The instantaneous fluid velocity <math> {u_i} </math> is decomposed into a mean part which is known (from turbulence model prediction) and a fluctuating part <math> {u_i}^{'} </math>. | ||
| + | So generating fluctuating part of the fluid velocity is the core of the problem. | ||
| + | Generation of the fluid particle velocity fluctuations is based on a Gaussian PDF for the fluid velocities, but different random schemes can then be used to guess the fluid velocity, which are characterized by the underlying fluid Lagrangian correlation function <math> {R_{fl}}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> {R_{fl}(\tau)}=\frac{\overline{{u}^{'}(t){u}^{'}(t+\tau)}}{{\sqrt{\overline{{u}^{'2}(t)}}}{\sqrt{\overline{{u}^{'2}(t+\tau)}}}} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The first approach was proposed by Gosman and Ioannides (1981) and has been called “eddy life time”. Each fluid velocity fluctuation is kept constant on a time step which is equal to the Lagrangian integral time scale <math> \tau_l </math>. The resulting Lagrangian correlation function is linearly decreasing from 1 to 0 in a time delay equal to <math> 2\tau_l </math>: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> {R_{fl}(\tau)}=1-\frac{\tau}{2\tau_l} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | A first extension has been proposed by Ormancey & Martinon (1984) and is commonly used in the Lagrangian community. In that scheme, a Poisson distribution of the time interval is introduced: each fluid velocity fluctuation is kept constant until a random number (uniformly distributed between 0 and 1) is smaller than <math> {\delta}{t} / {\tau_l} </math>. The resulting fluid Lagrangian correlation function is exponentially decreasing from 1 to 0: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> {R_{fl}(\tau)}=exp(\frac{-\tau}{\tau_l}) | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Later, Desjonqueres (1987) proposed a process which can handle any given correlation function. This can be done through a correlation matrix, as described by Berlemont et al (1990) or Boughattas et al. (2006). Moreover, Desjonqueres (1987) introduced the Frenkiel family of correlation function (1948) which are defined by: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> {R_{fl}(\tau)}=exp[\frac{-\tau}{(m^2+1)\tau_l}] cos[\frac{m\tau}{(m^2+1)\tau_l}] | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Where m is a loop parameter, giving the exponential decrease for m=0. | ||
| + | Let us note that this function presents negative loops and m=1 is the value used by Picart (1981) during confrontations of simulations with the experimental data. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Eddy Interaction Model === | ||
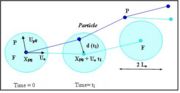
| + | Historically, the first approach which has been developed and widely used in engineering calculations is the Eddy Interaction Model, first described by Gosman and Ioannides (1981). In the Eddy Interaction Model, the discrete particle is assumed to interact with a succession of eddies. Each eddy is characterized by a velocity (fluctuating), a time scale (lifetime) and a length scale (size). | ||
| + | The fluid fluctuating velocity is randomly sampled with a Gaussian PDF of mean and variance that are deduced from turbulence model, as previously described. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Eddy interaction.JPG|thumb|Eddy Interation Model | ||
| + | (Graham & James 1996)]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The eddy life time and the eddy length scale can be estimated from the local turbulence properties and defined by: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> {l_{e}}={c_\mu^{3/4}} \frac{k^{3/2}}{\epsilon}=0.164\frac{k^{3/2}}{\epsilon} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>{t_{e}}=\frac{l_e}{u_f^{'}}=\frac{l_e}{\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}k}} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The time <math> {t_{c}}</math> for a particle to cross the eddy is calculated from the particle velocity (at the beginning of the time step) and the length scale <math> {l_{e}}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> {t_{c}}=-\tau_{p}ln[ 1- \frac{l_{e}}{\tau_{p} {\left|\vec u_f-\vec u_p \right|}}] | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The particle is assumed to interact with the eddy for a time which is the minimum of the eddy life time and the eddy transit time <math>{t_{c}}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>{t_{int}}={\delta}{t}={min({t_{e}},{t_{c}})}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | During that interaction the fluid fluctuating velocity is kept constant and the discrete particle is moved with respect to its equation of motion. Then a new fluctuating fluid velocity is sampled and the process is repeated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | unfortunately, the Eddy Interaction Model still cannot handle continuity effects. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Time Correlated Model === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Time_corrolated_model.JPG|thumb|Time Corrolated Model | ||
| + | (Burry & Bergeles 1993)]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Time_corrolated_berlemont.JPG|thumb|Time Corrolated Model | ||
| + | (Berlemont et al. 1991)]] | ||
| + | |||
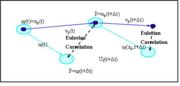
| + | The Correlated-Time Model, called also two-step methods is similar to the Eddy Interaction Model in a sense that the focus is also to solve the particle trajectory, the difference lies in how the fluctuating fluid velocity is determined along the particle trajectory. | ||
| + | this model takes into account the effect of the anisotropy of turbulence on the particulate phase. | ||
| + | |||
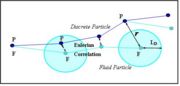
| + | The Correlated-Time Model is based on the simultaneous realization of a fluid trajectory and a particle trajectory. The fluid velocity is transferred from the fluid position to the particle position with respect to Eulerian correlation, and the process is then repeated (Burry & Bergeles 1993). | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is assumed that the fluid velocity at point <math>{P}</math> reads : | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>{{u}^{'}_p}={\gamma}{{u}^{'}_f}+{\sqrt{\overline{{u}^{'2}_p}}}{{\sqrt{{1-{\gamma}^{2}}}{y}}}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>{\gamma}=\frac{\overline{{{u}^{'}_p}{{u}^{'}_f}}}{{\sqrt{\overline{{u}^{'2}_p}}}{\sqrt{\overline{{u}^{'2}_f}}}}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | That approach has been extended by Berlemont et al. 1990. | ||
| + | he follow the two particle, monitoring their relative separation between time step, and only when the distance beteen them exceeds a certain length scale <math>{L_{D}}</math>,than the next fluid trajectory started from the present particle location. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This scheme is imaging the crossing trajectory effects in a very physical way, but it also allows incorporating the continuity effect through the Eulerian correlation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>{L_{D}}=\frac{L_{E11}+L_{E22}}{2}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>{L_{Eii}}={\sqrt{\overline{{u}^{'2}_i}}}{\tau_{li}}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>{\tau_{li}}=Cste\frac{\overline{{u}^{'2}_i}}{\epsilon}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Where <math>{Cste}</math> ranges between 0.2 and 0.6 | ||
| + | |||
| + | === One Step Model === | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | A third approach who mixed the Lagrangian and Eulerian step of the previous method, can also be defined to give a simpler stochastic scheme, but the probleme is then moved to the approximation of the time/length scales <math>{T^{*}}</math>,which characterize the fluid viewed by the particles. A Langevin equation is thus used: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>{{u}^{'}_{pi}(t+{\delta}{t})}={a}{{u}^{'}_{pi}}(t)+ by_i </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a=exp(\frac{ -{\delta}{t}} {{T^{*}_i}})</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>b={\sqrt{\overline{{u}^{'2}_{pi}(t)}}}{{\sqrt{{1-a^{2}}}}}</math> | ||
== Mixture model for two phase flow == | == Mixture model for two phase flow == | ||
| + | |||
=== Basics of the mixture model === | === Basics of the mixture model === | ||
| Line 22: | Line 134: | ||
=== VOF method === | === VOF method === | ||
| + | In computational fluid dynamics, the volume of fluid method (or in short VOF method) is a numerical technique for tracking and locating the free surface (or fluid-fluid interface). It belongs to the class of Eulerian methods which are characterized by a mesh that is either stationary or is moving in a certain prescribed manner to accommodate the evolving shape of the interface. | ||
| + | The VOF method is known for its ability to conserve the "mass" of the traced fluid, also, when fluid interface changes its topology, this change is traced easily, so the interfaces can for example join, or break apart. | ||
| + | The method is based on the idea of so called fraction function C. It is defined as the integral of fluid's characteristic function in the control volume (namely volume of a computational grid cell). Basically, when the cell is empty (there's no traced fluid inside) value of C is zero, if cell is full, we have C = 1, and when the interphasal interface cuts the cell, then 0 < C < 1. C is a discontinuous function, its value jumps from 0 to 1 when the argument moves into interior of traced phase. | ||
| + | The fraction function C is a scalar function, and while the fluid moves with velocity (in three-dimensional space ) every fluid particle retains its identity, i.e. when a particle is a given phase, it doesn't change the phase - like a particle of air, that is a part of air bubble in water remains air particle, regardless of the bubble movement (actually, for this to hold, we have to disregard processes such as dissolving of air in water). If that is so, then the substantial derivative of fraction function C needs to be equal to zero: | ||
| + | This is actually the same equation that has to be fulfilled by the level set distance function φ. | ||
| + | There are various means to solve this equation. It cannot be solved directly easily, since C is discontinuous, nevertheless such attempts have been performed. But most popular approach to the equation is the so called geometrical reconstruction, originating in the works of Hirt and Nichols. | ||
== Eulerian Two fluids approach == | == Eulerian Two fluids approach == | ||
| Line 33: | Line 151: | ||
== Conclusion == | == Conclusion == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | |||
| + | *{{reference-paper|author=Berlemont A., Desjonqueres PH., Guesbet G.|year=1990|title= Particle Lagrangian simulation in turbulent Flows|rest=Int. J. Multiphase Flow, 16-1, pp 19-34}} | ||
| + | *{{reference-paper|author=Boughattas N., Gazzah M. H., Said R.|year=2006|title=Effects of a co-flow on particles or droplets dispersion and on droplets vaporization in turbulent air flow |rest=ICAMEM2006, Hammamet, Tunisia}} | ||
| + | *{{reference-paper|author=Boughattas N., Gazzah M. H., Said R.|year=2007|title=Lagrangian prediction of particulate two-phase flow|rest=Fifth Mediterranean Combustion Symposium, Monastir, Tunisia}} | ||
| + | *{{reference-paper|author=Burry D., Bergeles G.|year=1993|title= Dispersion of particles in anisotropic turbulence|rest=Int. J. Multiphase Flow, 19-4, pp 651-664}} | ||
| + | *{{reference-paper|author=Desjonqueres PH.|year=1987|title= Modélisation Lagrangienne du comportement de particules discrètes en écoulement turbulent|rest=Thèse de doctorat, Faculté des Sciences de L’université de Rouen, France}} | ||
| + | *{{reference-paper|author=Graham D. I., James P. W.|year=1996|title= Turbulent dispersion of particles using eddy interaction models|rest=Int. J. Multiphase Flow, 22-1, pp 157-175}} | ||
| + | *{{reference-paper|author=Frenkiel F.N.|year=1948|title= Etude statistique de la turbulence - fonctions spectrales et coefficients de corrélation|rest=Rapport technique. ONERA n° 34}} | ||
| + | *{{reference-paper|author=Gosman A. D., Ionnides I. E.|year=1981|title=Aspects of computer simulation of liqued fuelled combustors|rest=AIAA aerospace sciences meeting, paper 81-0323, St.louis,MO}} | ||
| + | *{{reference-paper|author=Ormancey A., Martinon A.|year=1984|title= Prediction of particle dispersion in turbulent flows|rest=Physico-Chemical Hydrodynamics, 5-314, pp 229-244}} | ||
| + | *{{reference-paper|author=Picart A., Berlement A., Guesbet G.|year=1986|title= Modelling and predicting turbulence fields and the dispersion of discrete particles transported by turbulent Flows|rest=Int. J. Heat and Mass Transfer, 12-2, pp 237-261}} | ||
| + | *{{reference-paper|author=Hirt, C.W.; Nichols, B.D. (1981), "Volume of fluid (VOF) method for the dynamics of free boundaries", Journal of Computational Physics 39 (1): 201-225, doi:10.1016/0021-9991(81)90145-5}} | ||
Latest revision as of 11:38, 6 December 2010
Contents |
Introduction
article in progress
Importance of two phase flow in industrial configurations
Two phase flow phenomena occur in various industrial applications within all fluid mechanics application fields. Aerospace, automotive, nuclear applications, etc. In all these domains, it is important to predict two phase behavior. Prediction of liquid spray in an internal combustion engine allows for better control of the combustion process and helps to curtail pollutant emissions. Another important example involves steam equilibrium within a collar system; two flow analysis helps to prevent industrial accidents due to de-icing/anti-icing of aircraft on the ground etc. Any other examples can be quoted here.
Overview of the different available approach
Two main family can be distinguished to model two phase flow, depending of the two phase configuration approach. In case of dispersed configuration a lagrangian approach is suitable. Such an approach consists in following dropplets (or bubbles) during then movement. This is done by applying external force on the particle and solving acceleration, then velocity and finally position. On the other hand, two phase flow can be solve with an eulerien approach. As in all eulerian framework, this approach consists in considering inlet and outlet flux in a given volume. In such an eulerian approach, two family can be distinguished : Mixture model and Two fluids model, those two approach will be detailed in corresponding section bellow.
Lagrangian dispersed two-phase flow modelling
The main goal in Lagrangien approaches is to statiscally particle history in given flow fields. The starting point in Lagrangien approach is the fundamental law of dynamics:
Where 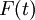 stands for the resulting force on the particle.
stands for the resulting force on the particle.
Resolution of these equations requires the knowledge of the instantaneous velocity of the fluid at particle position. The problem is thus to track fluid particles along the discrete particle trajectory.
A fluid particle instantaneously owns the velocity of the surrounding fluid and the simulation of its trajectory relies on a quite simple equation such as:

The instantaneous fluid velocity 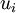 is decomposed into a mean part which is known (from turbulence model prediction) and a fluctuating part
is decomposed into a mean part which is known (from turbulence model prediction) and a fluctuating part 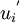 .
So generating fluctuating part of the fluid velocity is the core of the problem.
Generation of the fluid particle velocity fluctuations is based on a Gaussian PDF for the fluid velocities, but different random schemes can then be used to guess the fluid velocity, which are characterized by the underlying fluid Lagrangian correlation function
.
So generating fluctuating part of the fluid velocity is the core of the problem.
Generation of the fluid particle velocity fluctuations is based on a Gaussian PDF for the fluid velocities, but different random schemes can then be used to guess the fluid velocity, which are characterized by the underlying fluid Lagrangian correlation function 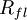 .
.
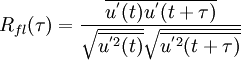
The first approach was proposed by Gosman and Ioannides (1981) and has been called “eddy life time”. Each fluid velocity fluctuation is kept constant on a time step which is equal to the Lagrangian integral time scale 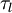 . The resulting Lagrangian correlation function is linearly decreasing from 1 to 0 in a time delay equal to
. The resulting Lagrangian correlation function is linearly decreasing from 1 to 0 in a time delay equal to 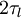 :
:
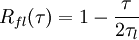
A first extension has been proposed by Ormancey & Martinon (1984) and is commonly used in the Lagrangian community. In that scheme, a Poisson distribution of the time interval is introduced: each fluid velocity fluctuation is kept constant until a random number (uniformly distributed between 0 and 1) is smaller than 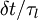 . The resulting fluid Lagrangian correlation function is exponentially decreasing from 1 to 0:
. The resulting fluid Lagrangian correlation function is exponentially decreasing from 1 to 0:
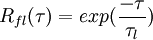
Later, Desjonqueres (1987) proposed a process which can handle any given correlation function. This can be done through a correlation matrix, as described by Berlemont et al (1990) or Boughattas et al. (2006). Moreover, Desjonqueres (1987) introduced the Frenkiel family of correlation function (1948) which are defined by:
![{R_{fl}(\tau)}=exp[\frac{-\tau}{(m^2+1)\tau_l}] cos[\frac{m\tau}{(m^2+1)\tau_l}]](/W/images/math/a/a/6/aa64bfd8d6f904364d7ef6bf12d2896a.png)
Where m is a loop parameter, giving the exponential decrease for m=0. Let us note that this function presents negative loops and m=1 is the value used by Picart (1981) during confrontations of simulations with the experimental data.
Eddy Interaction Model
Historically, the first approach which has been developed and widely used in engineering calculations is the Eddy Interaction Model, first described by Gosman and Ioannides (1981). In the Eddy Interaction Model, the discrete particle is assumed to interact with a succession of eddies. Each eddy is characterized by a velocity (fluctuating), a time scale (lifetime) and a length scale (size). The fluid fluctuating velocity is randomly sampled with a Gaussian PDF of mean and variance that are deduced from turbulence model, as previously described.
The eddy life time and the eddy length scale can be estimated from the local turbulence properties and defined by:
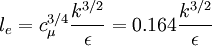
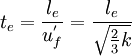
The time 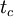 for a particle to cross the eddy is calculated from the particle velocity (at the beginning of the time step) and the length scale
for a particle to cross the eddy is calculated from the particle velocity (at the beginning of the time step) and the length scale 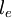 .
.
![{t_{c}}=-\tau_{p}ln[ 1- \frac{l_{e}}{\tau_{p} {\left|\vec u_f-\vec u_p \right|}}]](/W/images/math/0/8/b/08b7239e9ca63e74374305fc55098766.png)
The particle is assumed to interact with the eddy for a time which is the minimum of the eddy life time and the eddy transit time 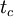 .
.
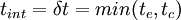 .
.
During that interaction the fluid fluctuating velocity is kept constant and the discrete particle is moved with respect to its equation of motion. Then a new fluctuating fluid velocity is sampled and the process is repeated.
unfortunately, the Eddy Interaction Model still cannot handle continuity effects.
The Correlated-Time Model, called also two-step methods is similar to the Eddy Interaction Model in a sense that the focus is also to solve the particle trajectory, the difference lies in how the fluctuating fluid velocity is determined along the particle trajectory. this model takes into account the effect of the anisotropy of turbulence on the particulate phase.
The Correlated-Time Model is based on the simultaneous realization of a fluid trajectory and a particle trajectory. The fluid velocity is transferred from the fluid position to the particle position with respect to Eulerian correlation, and the process is then repeated (Burry & Bergeles 1993).
It is assumed that the fluid velocity at point 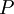 reads :
reads :
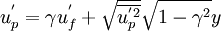
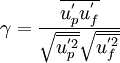
That approach has been extended by Berlemont et al. 1990.
he follow the two particle, monitoring their relative separation between time step, and only when the distance beteen them exceeds a certain length scale 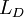 ,than the next fluid trajectory started from the present particle location.
,than the next fluid trajectory started from the present particle location.
This scheme is imaging the crossing trajectory effects in a very physical way, but it also allows incorporating the continuity effect through the Eulerian correlation.
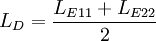
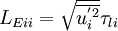
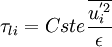
Where 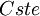 ranges between 0.2 and 0.6
ranges between 0.2 and 0.6
One Step Model
A third approach who mixed the Lagrangian and Eulerian step of the previous method, can also be defined to give a simpler stochastic scheme, but the probleme is then moved to the approximation of the time/length scales  ,which characterize the fluid viewed by the particles. A Langevin equation is thus used:
,which characterize the fluid viewed by the particles. A Langevin equation is thus used:
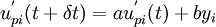
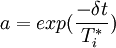
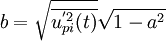
Mixture model for two phase flow
Basics of the mixture model
MAC approach
VOF method
In computational fluid dynamics, the volume of fluid method (or in short VOF method) is a numerical technique for tracking and locating the free surface (or fluid-fluid interface). It belongs to the class of Eulerian methods which are characterized by a mesh that is either stationary or is moving in a certain prescribed manner to accommodate the evolving shape of the interface. The VOF method is known for its ability to conserve the "mass" of the traced fluid, also, when fluid interface changes its topology, this change is traced easily, so the interfaces can for example join, or break apart. The method is based on the idea of so called fraction function C. It is defined as the integral of fluid's characteristic function in the control volume (namely volume of a computational grid cell). Basically, when the cell is empty (there's no traced fluid inside) value of C is zero, if cell is full, we have C = 1, and when the interphasal interface cuts the cell, then 0 < C < 1. C is a discontinuous function, its value jumps from 0 to 1 when the argument moves into interior of traced phase. The fraction function C is a scalar function, and while the fluid moves with velocity (in three-dimensional space ) every fluid particle retains its identity, i.e. when a particle is a given phase, it doesn't change the phase - like a particle of air, that is a part of air bubble in water remains air particle, regardless of the bubble movement (actually, for this to hold, we have to disregard processes such as dissolving of air in water). If that is so, then the substantial derivative of fraction function C needs to be equal to zero:
This is actually the same equation that has to be fulfilled by the level set distance function φ. There are various means to solve this equation. It cannot be solved directly easily, since C is discontinuous, nevertheless such attempts have been performed. But most popular approach to the equation is the so called geometrical reconstruction, originating in the works of Hirt and Nichols.
Eulerian Two fluids approach
Basics of the two fluids approach
Interfacial exchange closures
Turbulence modelling in such a context
Conclusion
References
- Berlemont A., Desjonqueres PH., Guesbet G. (1990), "Particle Lagrangian simulation in turbulent Flows", Int. J. Multiphase Flow, 16-1, pp 19-34.
- Boughattas N., Gazzah M. H., Said R. (2006), "Effects of a co-flow on particles or droplets dispersion and on droplets vaporization in turbulent air flow", ICAMEM2006, Hammamet, Tunisia.
- Boughattas N., Gazzah M. H., Said R. (2007), "Lagrangian prediction of particulate two-phase flow", Fifth Mediterranean Combustion Symposium, Monastir, Tunisia.
- Burry D., Bergeles G. (1993), "Dispersion of particles in anisotropic turbulence", Int. J. Multiphase Flow, 19-4, pp 651-664.
- Desjonqueres PH. (1987), "Modélisation Lagrangienne du comportement de particules discrètes en écoulement turbulent", Thèse de doctorat, Faculté des Sciences de L’université de Rouen, France.
- Graham D. I., James P. W. (1996), "Turbulent dispersion of particles using eddy interaction models", Int. J. Multiphase Flow, 22-1, pp 157-175.
- Frenkiel F.N. (1948), "Etude statistique de la turbulence - fonctions spectrales et coefficients de corrélation", Rapport technique. ONERA n° 34.
- Gosman A. D., Ionnides I. E. (1981), "Aspects of computer simulation of liqued fuelled combustors", AIAA aerospace sciences meeting, paper 81-0323, St.louis,MO.
- Ormancey A., Martinon A. (1984), "Prediction of particle dispersion in turbulent flows", Physico-Chemical Hydrodynamics, 5-314, pp 229-244.
- Picart A., Berlement A., Guesbet G. (1986), "Modelling and predicting turbulence fields and the dispersion of discrete particles transported by turbulent Flows", Int. J. Heat and Mass Transfer, 12-2, pp 237-261.
- Hirt, C.W.; Nichols, B.D. (1981), "Volume of fluid (VOF) method for the dynamics of free boundaries", Journal of Computational Physics 39 (1): 201-225, doi:10.1016/0021-9991(81)90145-5 ({{{year}}}), "{{{title}}}", {{{rest}}}.