Dynamic viscosity
From CFD-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
Littleandy (Talk | contribs) |
m |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
For the use in CFD, dynamic viscosity can be defined by different ways: | For the use in CFD, dynamic viscosity can be defined by different ways: | ||
* as a constant | * as a constant | ||
| - | * as a function of temperature (e.g. piecewise-linear, piecewise-polynomial, polynomial, by [[Sutherland's | + | * as a function of temperature (e.g. piecewise-linear, piecewise-polynomial, polynomial, by [[Sutherland's law]] or by the [[Power law]]) |
* by using [[Kinetic Theory]] | * by using [[Kinetic Theory]] | ||
* composition-dependent | * composition-dependent | ||
Revision as of 12:47, 17 May 2007
The SI unit of dynamic viscosity (Greek symbol: 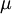 ) is the pascal-second (
) is the pascal-second (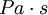 ), which is identical to
), which is identical to 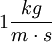 .
.
The dynamic viscosity is related to the kinematic viscosity by
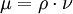
where 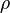 is the density and
is the density and 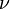 is the kinematic viscosity.
is the kinematic viscosity.
For the use in CFD, dynamic viscosity can be defined by different ways:
- as a constant
- as a function of temperature (e.g. piecewise-linear, piecewise-polynomial, polynomial, by Sutherland's law or by the Power law)
- by using Kinetic Theory
- composition-dependent
- by non-Newtonian models
