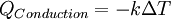Heat transfer
From CFD-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
(introduction to heat transfer) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Conduction == | == Conduction == | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Conduction can be defined as the heat transfer through a substance because of a temperature gradient. The rate of heat transfer by conduction between two regions of a substance is proportional to the thermal conductivity of the material and the temperature difference between them. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Mathematically, it can be described by using the Fourier's law: | ||
| + | :<math> | ||
| + | Q_{Conduction} = -k\Delta T | ||
| + | </math> | ||
Revision as of 03:04, 1 December 2005
Conduction
- Conduction can be defined as the heat transfer through a substance because of a temperature gradient. The rate of heat transfer by conduction between two regions of a substance is proportional to the thermal conductivity of the material and the temperature difference between them.
- Mathematically, it can be described by using the Fourier's law: